Nitration of Anizole
Nitration of Anizole:
The objective of this post is to understand the question
What are the products formed when methoxy benzene (Anisole) is subjected to nitration?
Let’s try to understand the concept associated with the Nitration of Anizole. The Mechanism is based on electrophilic substitution reaction
Anisole is a common name for Methoxy benzene and the structure of Methoxy benzene is as given below.

There is a – I effect on the Sigma bond between carbon and oxygen but oxygen is attached to an electron releasing group and has higher electron density as it already possesses lone pairs in two sp3 hybrid orbitals. Due to the presence of lone pairs on oxygen, it can share its electron density with the π-electron cloud of the benzene ring which is the +m effect.
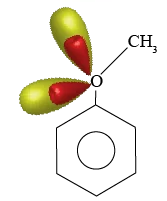
When methoxy benzene is treated with concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid mixture nitronium ions are produced and these nitronium ions are responsible for the nitration of methoxy benzene.

Methoxy benzene has three available positions where nitronium ions can attack the methoxy benzene and they are ortho, meta, and para positions as shown in the figure.

Nitronium ion equally attacks all the three available positions and corresponding resonating forms for all the three positions are shown below

In the resonating forms, structure I and structure II become exceptionally stable structures because the positive charge is present on the carbon atom which is attached to an electron releasing group thus relative stability of auto and para attacks in the methoxy benzene is much higher than meta attack. Thus in the case of methoxy benzene will nitration of methoxy benzene would always give ortho nitro methoxy benzene and para nitro methoxy benzene as major products.
In the above discussion, the stability of resonating forms is the most important criterion in deciding the formation of the product higher the stability of possible resonating forms greater the chances for the formation of that specific product. In di-substitution reactions of benzene or substituted arenes, the stability of resulting resonating forms is one of the most important factors in determining the formation of product
Check out reactions
| Chlorination Reaction | Bromination Reaction | Nitration Reaction |
| Sulphonation Reaction | Friedel Craft Alkylation Reaction | Friedel craft Acylation Reaction |
You may also like
| Nucleophilic Substitution reaction | Free Radical substitution reaction | Electrophilic addition reaction | Free radical addition reaction |
| Nucleophilic addition reaction | Elimination reaction | Bond Fission |
Our other courses
| Chemistry XII | Mock Test XI | Mock Test XII | |
| Mock Test NEET | Mock Test JEE Mains | Science class 9 |
Tag:CBSE
