Oxalic Acid against KMnO4
Oxalic Acid against KMnO4:
For Class 12 chemistry students, mastering the intricacies of titration is a crucial step toward understanding volumetric analysis and honing laboratory skills. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the fascinating world of volumetric titration, specifically focusing on the titration between oxalic acid and potassium permanganate (KMnO₄). This titration is not only a vital part of the chemistry curriculum but also serves as an exciting experiment that demonstrates the principles of redox reactions and quantitative analysis. Whether you’re preparing for your practical exams or seeking to reinforce your theoretical knowledge, this blog post will equip you with essential tips, step-by-step procedures, and valuable insights to ensure your practical experience is both educational and successful. Let’s unlock the secrets of titration and elevate your chemistry prowess with myetutors!
(Write on both sides the ruled and unruled Sheet)
Aim:
Prepare M/20 oxalic acid solution, and using this solution determine the strength of the given potassium permanganate (KMnO4) solution
(Write on unruled Sheet)
Chemical Equation:
In oxalic acid against KMnO4 titration KMnO4 acts as an oxidizing agent and Oxalic acid acts as a reducing agent. The reaction occurs in an acidic medium
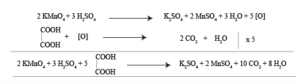
Indicator: KMnO4 acts as a self indicator
End Point / Color Change: Colorless to Light Pink
In oxalic acid against KMnO4 titration till MnO4 -1 ion is consumed in the solution the pink color disappears, but once MnO4 1- ion is in excess they impart a pink color to the solution
Observation Table:
In oxalic acid against KMnO4 titration, the observation table is as below
| S.No | Final Reading (in mL) | Initial Reading (in mL) | Difference | Concordant (mL) |
| 1 | 16.3 | 0.0 | 16.3 | 16.3 |
| 2 | 16.1 | 0.0 | 16.1 | |
| 3 | 16.3 | 0.0 | 16.3 |
Calculation:
In oxalic acid, against KMnO4 titration, the calculations are done as per the formula
a1M1V1 = a2M2V2
a1 = Moles of KMnO4 in balanced equation
M1 = Molarity of Oxalic Acid (M/20)
V1 = Volume of oxalic acid (Pipette volume)
a2 = Moles of Oxalic Acid in the balanced equation
M2 = Molarity of KMnO4 (To find out)
V2 = Volume of KMnO4 [Concordant volume (16.3 mL)]
Molarity of KMnO4
M2 = (a1M1V1)/ a2V2
Substitution values molarity of KMnO4 is
M2 = 0.0123 M
The calculation for the Strength of KMnO4:
Strength (in g/L) = Molarity x molecular weight of KMnO4
= 0.0123x 158 =1.938 gm /L
% Purity of KMnO4:
![]()
![]()
(Write on ruled Sheet)
Procedure:
- Preparation of 0.05 M Standard Solution of Oxalic Acid
- KMnO4 against Oxalic Acid titration.
- Clean the burette thoroughly, wash it with distilled water and finally rinse it with KMnO4 solution. (Always rinse the burette with the KMnO4 solution).
Clamp the burette vertically in a burette stand. - Fill KMnO4 solution into the burette through a funnel above the zero mark.
- Remove the air gap, if any, from the nozzle of the burette by running the solution forcefully from the burette nozzle.
- Remove the funnel before noting the initial reading of the burette. Also while noting the reading, see that no drop of the liquid is hanging at the nozzle of the burette.
- Note the initial reading by keeping the eye exactly at the same level as the meniscus of the solution.
- Pipette out 10 mL of oxalic acid solution in a washed and dried conical flask. Always wash the pipette with water and rinse with the oxalic acid (solution to be measured) before pipetting out the liquid.
- Place the flask over the glazed tile. Titrate the acid with KMnO4 solution
till a very faint permanent pink color is obtained. Add KMnO4 solution in small amounts initially and then dropwise
Result:
The strength of the given KMnO4 solution is 3.63 gm /L
Precautions:
The precautions for oxalic acid against KMnO4 titration
- Always rinse the burette with the solution, which is to be taken in it.
- Remove the air gap if any, from the burette before titrating the solution. Make sure that the nozzle of the burette is also filled.
- Never forget to remove the funnel from the burette before noting the readings of the burette and ensure that no drop is hanging from the nozzle of the burette.
- Always read the lower meniscus for all transparent solutions and the upper meniscus for colored solutions.
- To note the burette readings place the eye exactly at the level of the meniscus.
- Never hold the pipette at the bulb.
- Never use the pipette and burette with a broken nozzle.
- Never suck a strong acid or an alkali with the pipette.
- Always keep the lower end of the pipette dipped in the liquid while sucking the liquid.
- Do not blow out the last drop of the solution from the jet end of the pipette into the flask.
- The concentration (strength) of the solution must be calculated up to the fourth place of decimal.
You may also like
| Oxalic Acid against KMnO4 | Mohr Salt against KMnO4 | Sodium hydroxide against Oxalic Acid titration |
| Salt Analysis of NH4Cl | Salt Analysis of (NH4)2SO4 | Salt Analysis of (CH3COO)2Pb |
Latest Chemistry syllabus
